Thailand Privilege Card Co. Ltd. recently hosted a momentous event that unveiled an exhilarating new direction for the company. As you immersed yourself in the sleek interior of the Conrad Bangkok Hotel, the energy was palpable. Something special was in the air.
In this iconic setting, Thailand Privilege proudly introduced four meticulously designed Elite packages to replace their current offerings. These packages will take effect on October 1, spearheading a new era of luxury and privilege.
Humble Beginnings to Globally Renowned
It’s incredible to reflect on Thailand Privilege’s journey from welcoming 1,056 members between 2003-2005 to an astounding 31,500 members in 2023. Their tremendous growth shows no signs of slowing down.
Initially catering predominantly to affluent investors, the newly transformed Thailand Privilege aims to attract an even more diverse group of elites. From digital nomads and workcation enthusiasts to retirees and expats calling Thailand home, all will find a package tailored to their lifestyle.
Unlocking a World of Exclusive Benefits
As Thailand Privilege enters this new chapter, they are enhancing experiences for members through exclusive lifestyle privileges and signature touches. Allow yourself to be transported into the lap of luxury:
- Personal assistants adorned in elegant gold uniforms assist with your every need
- Let world-class Thai chefs tantalize your taste buds with customizable private dinners
- Luxury car airport transfers ensure maximum comfort and exclusivity
- Concierge services grant privileged access to government amenities
- Wealth management advisory provides insider perspectives into lucrative investments
- Premium healthcare package takes care of your wellbeing
- Complimentary stays at 5-star hotels let you experience Thailand in style
This is just a small taste of what’s to come. Thailand Privilege is leaving no stone unturned in curating once-in-a-lifetime privilege experiences.
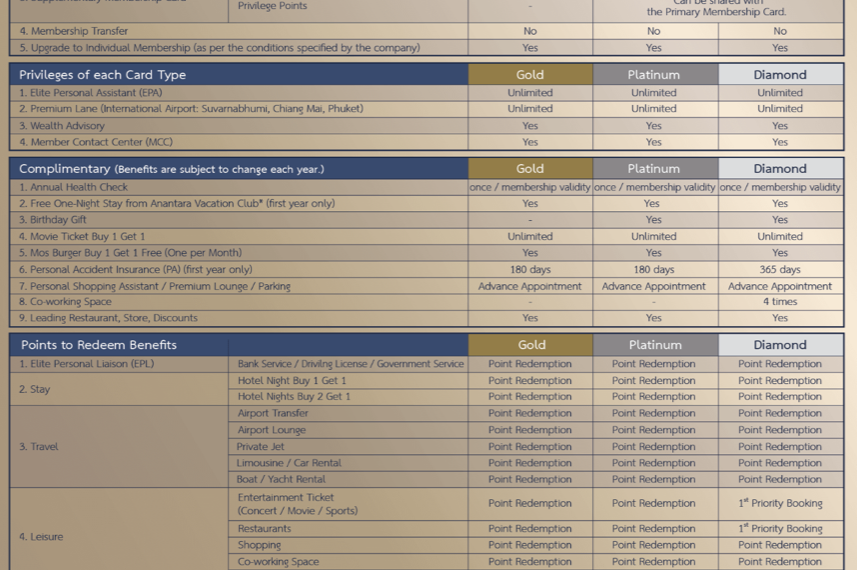
Four Elite Tiers Offer Bespoke Benefits
While these four tiers – Gold, Platinum, Diamond and Reserve – have their own personality, all providing pampering worthy of royalty.
As the presenter unveiled the specifics of each bespoke package, you could visualize the elevated lifestyle that would soon be within reach. Just imagine appreciating picturesque Thai sunsets as your private yacht cut through gentle turquoise waters. Bliss.
While every tier had its own flair, the Elite Reserve Membership’s air of prestige and exclusivity was unmatched. With only 100 spots available annually and a $142,000 price tag, this top-tier package grants insider access to the Reserve Club and other jaw-dropping benefits tailored specially for you.
Read more on these new Thailand Privilege cards available:
Privilege Takes on a Whole New Meaning
The grandeur of these new offerings shows that Thailand Privilege is entering an unprecedented golden era. By introducing privilege points and opportunities to redeem perks, they are enhancing membership flexibility like never before.
As the event drew to an inspiring close, the energy was electric. Attendees mingled with fervor, abuzz with visions of the privileged possibilities now laid before them in this new chapter for Thailand Privilege.
You glanced around, a smile creeping onto your face. This was just the beginning, both for Thailand Privilege and yourself.











 Donald Trump claimed during the election campaign that he would declare China a country manipulating his currency once he has become president and would impose heavy duties (up to 45%!) on US imports of Chinese goods.
Donald Trump claimed during the election campaign that he would declare China a country manipulating his currency once he has become president and would impose heavy duties (up to 45%!) on US imports of Chinese goods.